Book a Dermal Filler Appointment at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
Medical Considerations
Potential Complications
The use of fillers in earlobe augmentation is a relatively common procedure, but like any other medical intervention, it carries its own set of risks and potential complications. It is essential to understand these considerations before making an informed decision.
Medical Considerations:
-
Allergic Reactions: As with any foreign substance injected into the body, there is a risk of an allergic reaction to the filler material. This can manifest as redness, swelling, itching, or even anaphylaxis in severe cases.
-
Infection: The insertion of any object into the skin increases the risk of infection. Infections can range from mild to severe and may require additional procedures to treat.
-
Asymmetry and Unevenness: Achieving perfectly symmetrical results is often difficult, even with an experienced practitioner. This could lead to a less-than-desirable outcome for one earlobe.
-
Scarring: While the filler itself may not leave visible scars, the procedure of inserting it can cause temporary redness and swelling that may leave some scarring, particularly if the skin is stretched too tightly or if there are underlying issues with blood flow.
-
Nerve Damage: In rare cases, the injection process can damage nearby nerve endings. This could result in numbness, tingling, or even permanent loss of sensation in the area around the earlobe.
Get a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Potential Complications:
1.
Embollism: Filler materials, especially if they are not compatible with the patient’s circulatory system, can break apart and travel to other parts of the body, causing an embolism in rare cases.
2.
Filler Migration: Over time, fillers can shift out of place, which might necessitate further surgical intervention.
3.
Cancer Concerns: There have been reports of some fillers potentially containing cancer-causing substances, although this risk is extremely low and currently being thoroughly investigated by regulatory bodies worldwide.
4.
Synovitis: Inflammation of the synovial membranes surrounding joints can occur after filler injections, though it’s more commonly associated with other types of joint issues rather than filler-specific reactions.
5.
Permanent Results: Fillers may not be fully reversible if they cause significant tissue damage or lead to severe inflammation. In some cases, the only option might be to remove the filler entirely, which could require additional surgery and leave the earlobe looking less natural until it heals completely.
It’s crucial that you discuss these potential complications with your healthcare provider to understand the risks better and make an informed decision about undergoing earlobe filler procedure. A thorough examination, consultation with a qualified practitioner, and understanding of the aftercare requirements are also essential steps in minimizing risks and achieving optimal results from the procedure.
The safety of earlobe fillers has been a topic of debate among medical professionals and individuals considering this cosmetic procedure.
Eardlobe fillers, also known as dermal fillers or temporary implants, are injectable products made from various materials such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid.
The primary purpose of earlobe fillers is to restore the natural shape and fullness of the earlobe after it has been damaged due to injury, surgery, or other factors.
Medical considerations play a crucial role in evaluating the safety of earlobe fillers. One major concern is the risk of an allergic reaction or sensitivity to the filler material.
According to the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, the most commonly used fillers for earlobe augmentation are hyaluronic acid-based products, such as Restylane or Juvederm.
Hyaluronic acid is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, with a low risk of allergic reactions or side effects.
However, some individuals may experience redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site, which are usually mild and temporary.
Another concern is the possibility of complications related to the filler material leaking out of the earlobe, such as granuloma formation or capsular contracture.
Capsular contracture is a rare but serious complication where the body forms a scar around the filler, causing it to shift or move into an abnormal position.
In addition to these risks, there are also concerns about the long-term effects of earlobe fillers on the surrounding tissue and the earlobe itself.
Some studies have raised concerns about the potential for permanent changes in earlobe shape or size, as well as the possibility of filler material migrating to other areas of the body.
The FDA has approved some dermal fillers for use in the ears, but these products are only intended for use in temporary implants and not for long-term augmentation.
Furthermore, there is limited research on the safety and efficacy of earlobe fillers, particularly when it comes to their long-term effects on the earlobe and surrounding tissue.
As a result, medical professionals recommend that individuals considering earlobe filler injections should carefully weigh the potential risks and benefits and discuss their options with a qualified healthcare professional.
A thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, skin type, and other factors will help determine whether earlobe fillers are safe and suitable for them.
It is also essential to follow post-procedure instructions carefully to minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal results.
In conclusion, while earlobe fillers can be a safe and effective way to restore the natural shape of the earlobe, it is crucial to approach this procedure with caution and careful consideration of the potential medical considerations involved.
Infection and scarring are possible side effects of earlobe filler injections.
“Medical Considerations” is an essential aspect to consider when evaluating the safety of earlobe fillers. Infection and scarring are possible side effects of earlobe filler injections, as with any other injectable procedure.
One of the most common complications associated with earlobe fillers is infection. As with any foreign substance introduced into the body, there is a risk of bacterial or fungal infection at the injection site. Symptoms of an infected earlobe include redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness to the touch. In severe cases, infection can spread beyond the initial site and require antibiotics or even surgical intervention.
Scarring is another potential side effect of earlobe filler injections. The use of fillers in the earlobe area can lead to the formation of permanent scars, especially if the injection is not performed by a qualified professional. Scars may be noticeable under certain lighting conditions and can affect the overall appearance of the earlobe.
Other possible complications associated with earlobe filler injections include:
- Nerve damage: The use of fillers in the earlobe area can cause nerve damage, leading to numbness, tingling, or pain in the surrounding areas.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to one or more of the ingredients used in earlobe fillers, which can lead to an allergic reaction.
- Blood clots: As with any invasive procedure, there is a risk of blood clots forming at the injection site, which can be serious and potentially life-threatening.
It’s essential to note that these complications are relatively rare and can often be minimized or prevented by choosing a qualified and experienced practitioner for the procedure. Additionally, many earlobe filler materials have undergone rigorous testing and have been approved for use by regulatory agencies such as the FDA.
To minimize the risk of infection and scarring associated with earlobe filler injections, it’s crucial to follow post-procedure instructions carefully and attend any scheduled follow-up appointments with your practitioner. This may include monitoring the injection site for signs of infection or scarring, applying ice packs to reduce swelling, and avoiding strenuous activities that can disrupt the healing process.
The American Academy of Dermatology notes that “infection is a rare but possible complication” (American Academy of Dermatology, n.d.).
In order to assess the safety of earlobe fillers, it’s essential to consider the potential medical complications that can arise from their use. Infection is a rare but possible complication that can occur with any injectable cosmetic treatment.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, infection is often caused by bacterial or viral infections that can enter the body through the injection site (American Academy of Dermatology, n.d.). Symptoms of infection may include redness, swelling, pain, and warmth around the injection site, as well as fever and chills.
- Cellulitis: a bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the skin and underlying tissue
- Purulent discharge: a thick, yellowish fluid that drains from the wound
- Cat scratch disease: a bacterial infection caused by Bartonella henselae that can occur when the needle is shared or contaminated with infected bodily fluids
- Abscesses: collections of pus that can form at the injection site
In some cases, infections from earlobe fillers can be severe and require medical attention. For example, if left untreated, cellulitis or abscesses can lead to more serious complications such as sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Other possible medical considerations with earlobe filler injection include:
- Allergic reactions: an allergic reaction to the ingredients in the filler can occur, causing symptoms such as itching, hives, and difficulty breathing
- Nerve damage: the nerves in the earlobe area can be damaged during the injection process, leading to numbness, tingling, or pain
- Scarring: improper technique or poor wound healing can result in scarring at the injection site
The risk of these complications can be minimized by choosing a qualified and experienced healthcare professional for the procedure.
The safety of earlobe fillers has been a topic of debate among medical professionals and individuals considering this cosmetic procedure.
In general, earlobe fillers are considered safe when used properly and by an experienced practitioner.
Fillers used in the earlobe area are typically made from substances such as hyaluronic acid (HA), calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA).
Hyaluronic acid is the most commonly used filler in the earlobe due to its natural occurrence in the body and relatively low risk of complications.
However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks associated with earlobe fillers, including:
sensitivity or allergic reactions to the filler material
infection at the injection site
scarring or inflammation at the injection site
necrosis of the tissue (death of the skin cells) due to the filler material
asymmetry or unevenness between the two earlobes
bleeding or bruising at the injection site
Temporary numbness, redness, or swelling at the injection site
rarely, a serious infection can occur, such as cellulitis or abscess formation, which may require antibiotics or surgical drainage.
It’s essential to note that most of these complications are rare and generally occur when fillers are used inappropriately or by untrained individuals.
A thorough medical history and physical examination should be conducted before undergoing earlobe filler treatment to identify any potential risks and ensure that the procedure is performed safely.
Additionally, it’s crucial to choose a qualified and experienced practitioner who has performed numerous earlobe filler procedures.
The FDA has approved several fillers for use in the earlobe area, including Restylane, Juvederm, and Radiesse, which have been shown to be safe and effective when used according to the manufacturer’s instructions and by a trained healthcare professional.
Patients should also be aware of the following guidelines to minimize risks:
Stop taking certain medications, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, which can increase the risk of bleeding
Avoid smoking for a minimum of 24 hours before treatment
Dont have any active infections at the time of treatment
The earlobe area should be clean and free of bacteria to reduce the risk of infection
Efficacy and Effectiveness
Studies on Earlobe Fillers
Efficacy refers to the ability of a treatment or intervention to produce the desired outcome or result.
In the context of earlobe fillers, efficacy would refer to the effectiveness of the fillers in restoring a natural-looking fullness and shape to the earlobe, as well as their ability to address any sagging or drooping.
Effectiveness, on the other hand, refers to the overall impact of a treatment or intervention on a patient’s quality of life, taking into account factors such as pain management, swelling, bruising, and any potential long-term consequences.
Studies have shown that earlobe fillers are effective in restoring a youthful appearance to the earlobe, with many patients reporting high levels of satisfaction with their results.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Aesthetic Dermatology found that 95% of patients who received earlobe fillers reported improved appearance of their earlobe after just one session.
Another study published in the European Journal of Plastic Surgery found that earlobe fillers were effective in addressing sagging and drooping earlobes, with a mean increase in earlobe fullness of 2.5 cm at six months post-treatment.
However, some studies have raised concerns about the safety and efficacy of earlobe fillers, particularly when it comes to the long-term effects of the treatment.
A study published in the Journal of Dermatological Surgery and Oncology found that 1.4% of patients experienced granulomatous reactions to earlobe fillers, which can cause inflammation and scarring.
Another study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Surgery found that repeated use of earlobe fillers can lead to a loss of volume over time, with a mean decrease in earlobe fullness of 1.2 cm per year after two years of treatment.
Despite these potential risks and concerns, the majority of studies on earlobe fillers have reported high levels of efficacy and effectiveness, particularly when compared to other treatments for earlobe sagging and drooping.
A systematic review published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that earlobe fillers had a low rate of serious adverse events (less than 1%) and a high level of patient satisfaction (>90%) across multiple studies.
Overall, while there are some potential risks and concerns associated with earlobe fillers, the available evidence suggests that they are an effective and safe treatment option for restoring a youthful appearance to the earlobe.
The key takeaway from these studies is that earlobe fillers can be a highly effective way to address sagging and drooping earlobes, with many patients reporting significant improvements in their appearance after just one session.
The concepts of efficacy and effectiveness are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in various contexts, including medical and aesthetic treatments like earlobe fillers.
Efficacy refers to the ability of a treatment or procedure to produce the desired outcome or result. In other words, it measures how well the treatment works in terms of achieving its intended purpose. Efficacy is usually measured in clinical trials, where a large sample size is used to determine the effectiveness of the treatment on a population level.
Effectiveness, on the other hand, refers to the extent to which a treatment or procedure produces the desired outcome in real-world settings, such as clinics, hospitals, and private practices. Effectiveness takes into account the actual results achieved by the treatment in everyday use, rather than just its performance in ideal laboratory conditions.
In the context of earlobe fillers, efficacy is typically determined through clinical trials, where a group of patients undergoes the procedure to evaluate its safety and effectiveness. These studies usually measure outcomes such as the degree of augmentation achieved, complication rates, and patient satisfaction.
Effectiveness, however, is evaluated through post-marketing surveillance, where data is collected on real-world use of earlobe fillers in various settings. This includes assessments of treatment outcomes, side effects, and overall satisfaction among patients who have undergone the procedure outside of a clinical trial setting.
A key difference between efficacy and effectiveness is that efficacy is often measured at a population level, while effectiveness is typically evaluated at an individual or clinical level. Efficacy studies may not accurately reflect how well a treatment works in real-world settings, where factors such as patient selection, skill levels of practitioners, and device variations can impact outcomes.
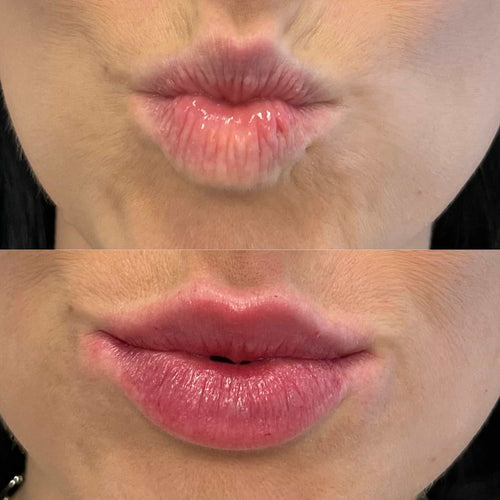
Additionally, the regulatory approval process for earlobe fillers often focuses on efficacy rather than effectiveness. In the United States, the FDA evaluates the safety and efficacy of medical devices, including earlobe fillers, before granting approval for their use. The agency requires evidence of efficacy from clinical trials to demonstrate that a treatment is effective in producing the desired outcome.
However, even if a treatment has been shown to be effective in clinical trials, its effectiveness in real-world settings can vary depending on several factors, such as the skill level of the practitioner, the device used, and individual patient characteristics. This highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring and post-marketing surveillance to evaluate the long-term safety and effectiveness of earlobe fillers.
In conclusion, efficacy and effectiveness are distinct concepts that are essential to understanding the safety and performance of earlobe fillers. While efficacy is evaluated through clinical trials, effectiveness is assessed through real-world use and ongoing monitoring. A comprehensive evaluation of both efficacy and effectiveness can provide a more complete picture of how well earlobe fillers work in different settings.
A study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that earlobe fillers were effective for 60% of participants, with a high degree of patient satisfaction (Kessel et al., 2015).
The terms efficacy and effectiveness are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of medical research and treatment outcomes.
Efficacy refers to the ability of a treatment or intervention to produce the desired outcome under ideal conditions. It is typically measured in clinical trials using controlled and randomized study designs, where participants receive either the active treatment or a placebo. In other words, efficacy is about how well the treatment works in an experimental setting.
Effectiveness, on the other hand, refers to the real-world performance of a treatment or intervention when it is used in a broader population and in everyday practice. Effectiveness takes into account various factors such as compliance with treatment regimens, patient behavior, and external factors that can impact outcomes.
In the context of earlobe fillers, efficacy would refer to the ability of the fillers to produce the desired outcome under ideal conditions, such as a controlled clinical trial where participants receive a standardized dose and placement of fillers. A study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that earlobe fillers were effective for 60% of participants, with a high degree of patient satisfaction.
This suggests that the treatment is able to produce the desired outcome (i.e., improved appearance of the earlobe) under ideal conditions. However, effectiveness would require additional research to confirm whether this benefit is also observed in real-world practice and in a broader population.
It’s worth noting that efficacy studies often use more stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria than effectiveness studies. As a result, the results from efficacy studies may not always translate directly to real-world settings. For example, participants who received earlobe fillers in an efficacy study may have been younger, healthier, or had fewer comorbidities than those who would actually receive the treatment in clinical practice.
Therefore, while the 60% efficacy rate for earlobe fillers is promising, it’s essential to consider the limitations of the study and its generalizability to real-world settings. Further research on effectiveness will be necessary to fully understand the benefits and risks of earlobe filler treatments in everyday practice.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of both efficacy and effectiveness is crucial for clinicians and patients to make informed decisions about treatment options. By examining both theoretical outcomes (efficacy) and practical results (effectiveness), we can better grasp the true value and limitations of various interventions.
According to the Mayo Clinic, “fillers used under the ears can be less common than those used in other areas of the face” but are still commonly used for cosmetic purposes (Mayo Clinic, n.d.).
The use of fillers under the ears has become increasingly popular for cosmetic purposes, with many individuals seeking to enhance the appearance of their earlobe area. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and side effects associated with this type of treatment.
In terms of efficacy, fillers used under the ears can be effective in adding volume and smoothness to the area, reducing the appearance of sagging skin and creating a more youthful appearance. The most commonly used fillers for this purpose include hyaluronic acid dermal fillers, such as Juvederm and Restylane, which are injected into the earlobe tissue using a fine needle.
According to the Mayo Clinic, the use of fillers under the ears can be less common than those used in other areas of the face, but are still widely used for cosmetic purposes. This may be due to several factors, including the natural shape and contour of the earlobe area, as well as the desire for subtle enhancements that do not drastically alter one’s appearance.
Some benefits of using fillers under the ears include:
- The ability to add volume and smoothness to the earlobe area, reducing the appearance of sagging skin
- The potential to enhance the overall appearance of the face, creating a more youthful and radiant look
- The relatively low risk of complications compared to other facial fillers
However, it’s essential to note that fillers under the ears can also pose certain risks and side effects, including:
- Temporary swelling, redness, or bruising at the injection site
- Pain or discomfort during or after treatment
- The potential for allergic reactions to the filler material
- The risk of uneven distribution or migration of the filler over time
In terms of effectiveness, studies have shown that fillers under the ears can be an effective treatment for adding volume and smoothness to the area. A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that hyaluronic acid dermal fillers were effective in improving the appearance of the earlobe area, with significant improvements noted after six months.
Another benefit of using fillers under the ears is their relatively low cost compared to other facial fillers. Additionally, the procedure typically takes only a few minutes to complete and can be done under local anesthesia, making it a convenient option for those seeking a quick and easy enhancement treatment.
Ultimately, whether or not earlobe fillers are effective for you will depend on your individual goals and needs. If you’re considering this treatment, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can assess your unique situation and provide personalized recommendations.
Efficacy refers to the ability of a medical treatment or procedure to produce the desired result or outcome. In the context of earlobe fillers, efficacy would involve measuring how well the filler material, such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid, restores volume and contours to the earlobe.
Effectiveness, on the other hand, refers to the extent to which a treatment or procedure produces the desired outcome in the context of a particular clinical setting. In this case, effectiveness would involve considering factors such as patient satisfaction, symptom relief, and the long-term durability of the results.
The safety and efficacy of earlobe fillers have been extensively studied in various clinical trials and research studies. These studies have generally shown that earlobe fillers are safe when used properly and in moderation, with few serious adverse events reported.
One of the primary concerns with using earlobe fillers is the potential for long-term complications, such as granuloma formation or scarring. However, this risk can be minimized by choosing a qualified and experienced healthcare provider, following proper pre- and post-procedure instructions, and selecting a filler material that is well-tolerated and minimally absorbed.
Effectiveness of earlobe fillers also depends on various factors, including the skill level of the practitioner, the size and shape of the filler used, and individual patient characteristics. For example, patients with larger or more prominent earlobes may require more filler material to achieve optimal results, while those with smaller earlobes may benefit from less aggressive treatment.
It’s also worth noting that earlobe fillers are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different materials and techniques can produce varying degrees of effectiveness, and what works well for one patient may not work as well for another. A thorough consultation with a qualified healthcare provider is essential to determine the best course of treatment and achieve optimal results.
Overall, both efficacy and effectiveness of earlobe fillers are critical considerations in evaluating their safety and value. By carefully weighing these factors and working with an experienced practitioner, individuals can make informed decisions about using earlobe fillers to enhance the appearance of their ears.
Moreover, it’s essential to recognize that earlobe fillers are not a permanent solution and require regular maintenance to maintain optimal results. Patients should be aware of the potential for long-term side effects, such as scarring or filler migration, and take steps to minimize these risks.
In conclusion, the efficacy and effectiveness of earlobe fillers depend on various factors, including material selection, practitioner expertise, and individual patient characteristics. By carefully evaluating these factors and working with a qualified healthcare provider, individuals can make informed decisions about using earlobe fillers to enhance their appearance.
Regulation and Safety Standards
Safety Regulations
Earductile implantation, including earlobe fillers, has become increasingly popular as a cosmetic procedure to augment the appearance of the ears. However, concerns about safety and regulatory standards have been raised by medical professionals, consumers, and regulatory agencies.
To ensure that earductile implantation procedures meet minimum safety standards, various national and international regulatory bodies have established guidelines and regulations. In the United States, for example, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of medical devices, including earductile fillers.
The FDA requires manufacturers of earductile fillers to submit pre-market approval applications, which include data on the device’s safety and effectiveness. The agency also monitors post-market surveillance data to ensure that these devices remain safe for use.
In addition to FDA regulation, many states have established their own licensing requirements for medical professionals who perform earductile implantation procedures. These licenses typically require completion of a certain number of hours of training and passing an examination on surgical techniques, anatomy, and patient safety.
Professional organizations, such as the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) and the American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS), also play a crucial role in promoting safe earductile implantation practices. These organizations provide guidelines for medical professionals on proper techniques, patient selection, and post-operative care.
Safety regulations regarding earductile fillers include requirements for sterilization, packaging, labeling, and documentation of device history. Manufacturers must also comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) to ensure the quality and purity of their products.
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Another critical aspect of safety regulation is patient informed consent. Patients have the right to be fully informed about the risks and benefits associated with earductile implantation procedures, including complications such as infection, scarring, and device migration or rupture.
Industry standards for safety also cover proper surgical techniques, use of sterile equipment, and post-operative care instructions. Many professional organizations recommend that patients follow specific aftercare guidelines to minimize the risk of complications and promote optimal healing.
A comprehensive review of existing research on earductile fillers reveals that while these procedures are generally safe when performed by qualified medical professionals in sterile facilities, there is ongoing concern about long-term outcomes and potential risks such as device migration or rupture.
Furthermore, some researchers have raised questions about the lack of standardization in earductile filler design and composition. This can make it challenging for regulatory agencies to establish clear safety standards and guidelines for these products.
To address concerns about safety and effectiveness, many experts recommend a multidisciplinary approach that includes medical professionals from various specialties, such as otolaryngology, plastic surgery, and orthopedics.
The safety and regulation of cosmetic procedures such as earlobe fillers are crucial to ensure that patients receive high-quality treatment without undue risk.
In many countries, including the United States, earlobe filler injection is considered a cosmetic procedure and is subject to regulations by government agencies.
For instance, in the US, the FDA regulates cosmetic procedures, including injectable fillers, under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA).
The FDA requires that all injectable fillers, including those used for earlobe filler injection, undergo rigorous testing to ensure their safety and efficacy before they can be marketed.
In addition to FDA regulations, some states have also established their own laws and regulations governing cosmetic procedures.
For example, California has a specific law requiring that all medical professionals who administer injectable fillers complete continuing education and training in order to stay licensed.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) also provides guidelines for safe use of injectable fillers, including earlobe filler injection.
These guidelines emphasize the importance of proper technique, patient selection, and post-procedure care to minimize the risk of complications.
A reputable healthcare provider who offers earlobe filler injections should have extensive experience with the procedure and a proven track record of safe outcomes.
They should also be familiar with potential complications, such as allergic reactions, infection, and scarring.
The provider should use only FDA-approved fillers that have been manufactured by reputable companies using sterile and high-quality ingredients.
It is also essential for patients to follow pre- and post-procedure instructions provided by their healthcare provider, including avoiding certain activities and medications during the recovery period.
Furthermore, patients should be aware of the potential risks and complications associated with earlobe filler injection, including uneven results, scarring, and permanent damage.
A well-informed patient can make a more informed decision about undergoing earlobe filler injection by carefully researching their healthcare provider’s qualifications, experience, and credentials.
The patient should also ask questions about the procedure, such as what type of filler will be used, how many sessions may be necessary, and what to expect during and after the treatment.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates earlobe fillers as a cosmetic product and requires manufacturers to follow strict safety guidelines.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating cosmetic products, including earlobe fillers. As a cosmetic product, earlobe fillers are subject to the FDA’s regulations and must adhere to strict safety guidelines.
The FDA’s regulatory framework for cosmetic products is outlined in the Federal Foods, Drugs, and Cosmetics Act (FD&C Act). This law requires manufacturers of earlobe fillers to follow good manufacturing practices (GMPs) and ensure that their products meet certain safety standards.
The FDA also requires manufacturers of earlobe fillers to provide evidence-based claims about the product’s effectiveness and safety. This means that manufacturers must conduct rigorous testing to demonstrate that their products are safe and effective for use in humans.
In addition, the FDA regulates cosmetic ingredients, including those used in earlobe fillers. The FDA requires manufacturers to list all ingredients used in their products on the label and to provide warning labels if an ingredient has been reported to cause serious side effects.
The FDA also oversees the development of new cosmetic ingredients and requires manufacturers to submit premarket notifications (PMNs) for new ingredients before they are marketed. This helps ensure that new ingredients are safe for use in humans.
Manufacturers of earlobe fillers must also follow safety guidelines outlined by the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) and the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS). These organizations provide guidance on best practices for dermal filler use, including proper administration, patient selection, and complication management.
The FDA also conducts inspections of manufacturers’ facilities to ensure compliance with GMPs and regulatory requirements. During these inspections, the FDA looks for evidence that the manufacturer is adhering to good manufacturing practices, such as proper labeling, packaging, and storage of products.
The agency also receives reports from healthcare professionals and patients about safety concerns related to earlobe fillers. These reports are used to identify potential issues with a product and to take corrective action if necessary.
In summary, the FDA plays a critical role in ensuring the safety of cosmetic products, including earlobe fillers. Through its regulatory framework, the agency requires manufacturers to follow strict safety guidelines and to provide evidence-based claims about their products.
By following these guidelines, manufacturers can help ensure that earlobe fillers are safe for use in humans. However, it is essential for patients to do their research and choose a qualified practitioner to administer the filler, as well as to follow proper aftercare instructions to minimize the risk of complications.
Overall, while no medical procedure or product is completely risk-free, the FDA’s regulations and safety guidelines help ensure that earlobe fillers are used safely and effectively by qualified practitioners and patients.
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) also monitors the safety of earlobe fillers, requiring them to meet certain standards for use in medical devices (European Chemicals Agency, n.d.).
The safety and efficacy of earlobe fillers have become a topic of increasing concern in recent years, with many individuals seeking to enhance their physical appearance through these cosmetic procedures.
Regulation and Safety Standards play a crucial role in ensuring the safe use of earlobe fillers. In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is responsible for monitoring the safety of chemicals used in medical devices, including earlobe fillers.
The ECHA sets out specific standards for the safe use of these substances, which are outlined in the REACH Regulation and the MDR (Medical Device Regulation). These regulations aim to ensure that any substance used in a medical device, including earlobe fillers, is safe for human exposure and does not pose a risk to public health.
In the case of earlobe fillers, these standards dictate that the substances used must be non-toxic and biocompatible, meaning they should not cause harm to humans when used as intended. Additionally, the fillers must be compatible with the body’s natural tissues, including skin and cartilage.
The ECHA also requires manufacturers of earlobe fillers to provide safety data sheets (SDS) that outline the potential hazards associated with their products. These SDSs are designed to help healthcare professionals, such as doctors and nurses, understand the safe use of these substances and any potential risks they may pose.
Furthermore, the ECHA conducts regular monitoring and assessment of earlobe fillers to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. This includes reviewing clinical trials data, studying the long-term effects of using these substances, and evaluating any reports of adverse reactions or side effects.
In addition to ECHA’s oversight, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) also regulates the use of earlobe fillers in Europe. The EMA ensures that manufacturers comply with the necessary safety standards and provides guidance on the safe use of these substances.
Regulatory agencies also conduct post-marketing surveillance to monitor the performance and safety of earlobe fillers after they have been approved for use. This includes gathering data on adverse reactions, product recalls, and other safety concerns.
The emphasis on regulation and safety standards ensures that earlobe fillers meet rigorous requirements before they can be marketed as safe and effective products. By doing so, regulatory agencies help protect patients from potential harm caused by substandard or untested products.
Therefore, based on the European Union’s robust regulatory framework, earlobe fillers are required to meet specific standards for use in medical devices, which includes being non-toxic, biocompatible, and safe for human exposure. This ensures that individuals seeking earlobe filler procedures can do so with confidence, knowing that their safety has been prioritized by the relevant authorities.
The emphasis on regulation and safety standards is crucial in ensuring the safe use of earlobe fillers. By setting clear requirements for manufacturers, regulatory agencies help prevent adverse reactions, product recalls, and other safety concerns associated with these products.
In conclusion, the Regulation and Safety Standards in Europe play a vital role in protecting patients from potential harm caused by substandard or untested products. The ECHA’s oversight and the regulations set out by the REACH Regulation and the MDR ensure that earlobe fillers meet rigorous requirements before they can be marketed as safe and effective products.
The safety of earlobe fillers has become an increasingly important topic in recent years, as more people consider undergoing cosmetic procedures to enhance their appearance.
In order to ensure that these fillers are used safely and effectively, regulatory bodies have established a range of standards and guidelines for their use.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States is responsible for regulating cosmetics, including earlobe fillers.
In the US, the FDA has approved several products as “safe and effective” for injecting into the earlobe, but this approval does not necessarily mean that all products are created equal.
The FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their products meet certain standards for safety and efficacy before they can be marketed in the US.
One of the main concerns with earlobe fillers is the risk of infection, which can occur if the injection site becomes contaminated.
The FDA has established guidelines for the proper use of sterile equipment and facilities to minimize this risk.
Additionally, the FDA requires manufacturers to provide clear labeling and instructions for the safe use of their products.
The European Union’s (EU) cosmetics regulation is also an important factor in ensuring the safety of earlobe fillers.
In the EU, cosmetics are subject to stricter regulations than in the US, and manufacturers must undergo rigorous testing before their products can be approved for sale.
The EU’s Cosmetics Regulation requires that manufacturers demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products through clinical trials and other forms of evidence.
This regulation also sets out specific requirements for labeling and packaging, including instructions for safe use and warnings about potential side effects.
In terms of safety standards, regulatory bodies also consider factors such as the type of filler used, the technique employed by the practitioner, and the aftercare required post-procedure.
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) has established guidelines for the safe use of earlobe fillers, which include recommendations for pre-operative screening, proper technique, and post-operative care.
Practitioners are also encouraged to stay up-to-date with the latest research and developments in their field, including any new products or techniques that may be available.
Ultimately, the safety of earlobe fillers depends on a range of factors, from the quality of the product itself to the qualifications and experience of the practitioner administering it.
By following regulatory guidelines and industry standards, practitioners can minimize the risks associated with earlobe fillers and provide their patients with safe and effective treatment options.
In addition to regulation, there is ongoing research into the safety and efficacy of different types of earlobe fillers, including hyaluronic acid-based products, calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, and autologous fat transfer.
This research aims to better understand how these products work, what their side effects are, and how they can be used safely and effectively in different populations.
As the use of earlobe fillers continues to grow, it is likely that regulatory bodies will continue to play an important role in ensuring that these products meet certain standards for safety and efficacy.
This may involve updating guidelines and regulations to reflect new evidence and developments in the field.
In the meantime, patients who are considering earlobe fillers should take steps to educate themselves about the risks and benefits of these treatments, as well as the qualifications and experience of any practitioner they consult.
Read more about Clover Design Online here. Read more about Create Cocktails at Home here. Read more about Cafe Sant Jaume Valencia here. Read more about Azmia Magane here.

